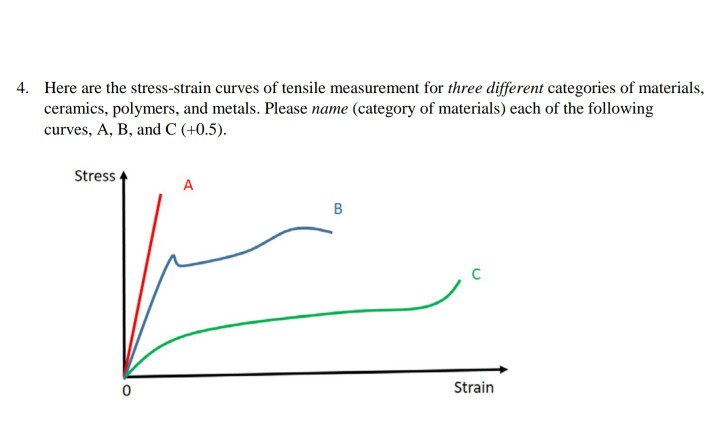
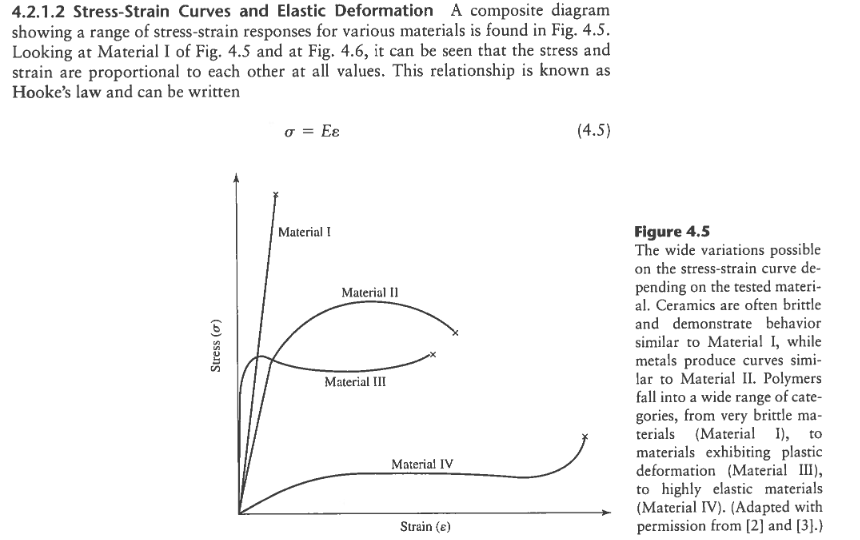
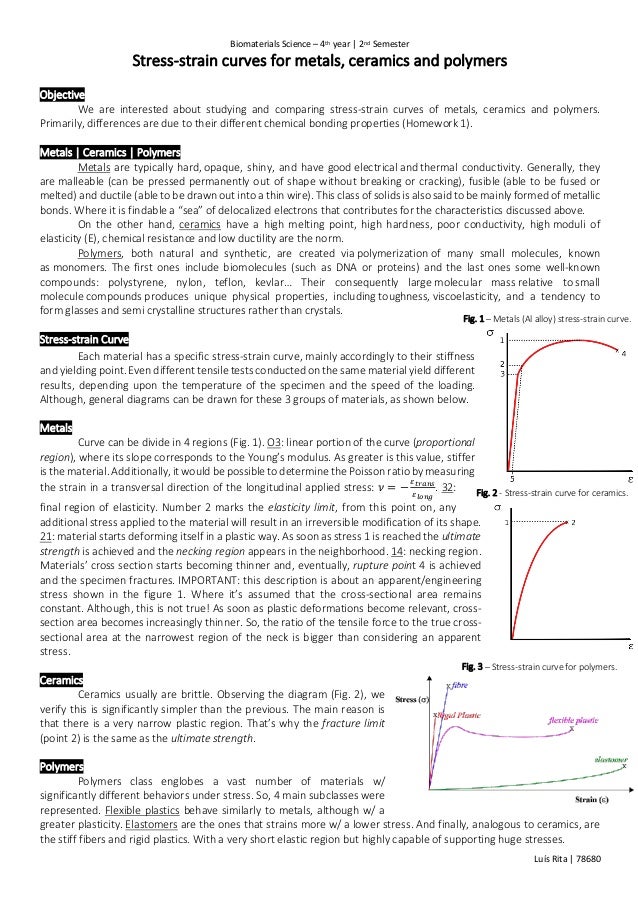
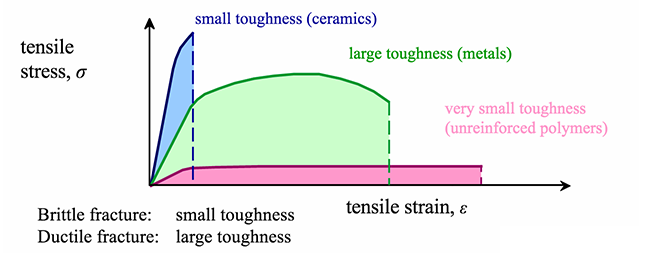
Ceramic Vs Metal Stress Strain Curve
Depending on strain the flow stress of the alloy may be higher or lower than that of the base metal.
Ceramic vs metal stress strain curve. Ceramic pores vs flexural strength. Stress strain curves of typical solid solution crystals with a stacking fault energy sfe lower than that of the base metal are shown in fig. Occurs when polymer backbones are aligned and about to break σ y engineering typical response of a metal ts stress engineering strain. The stress strain curve in this part of the graph is almost horizontal which implies that there is an appreciable increase in strain for a negligible increase in stress.
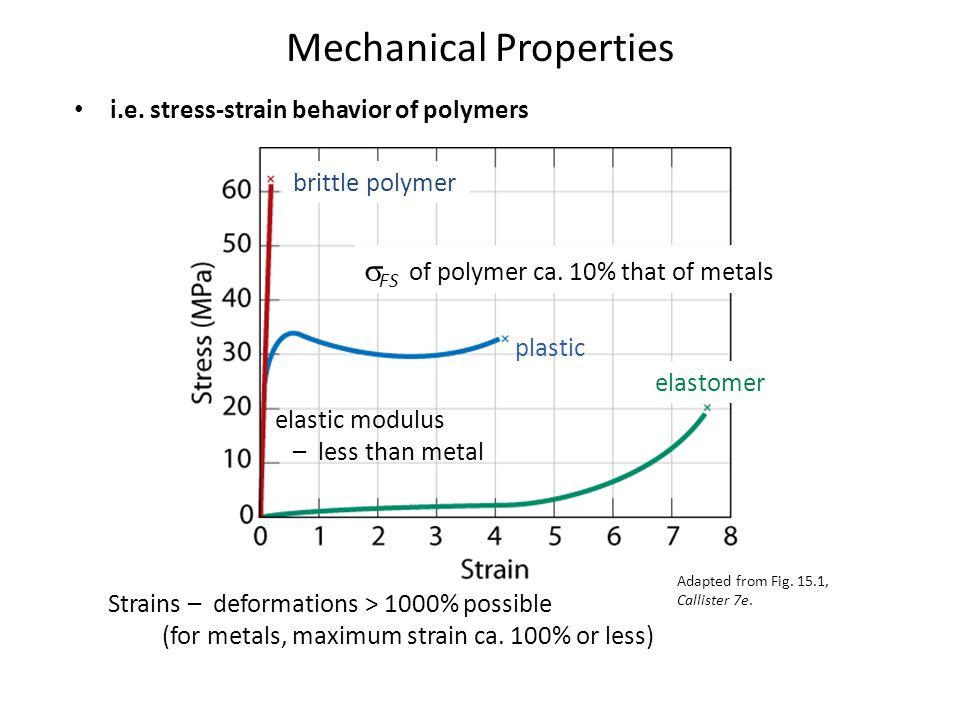
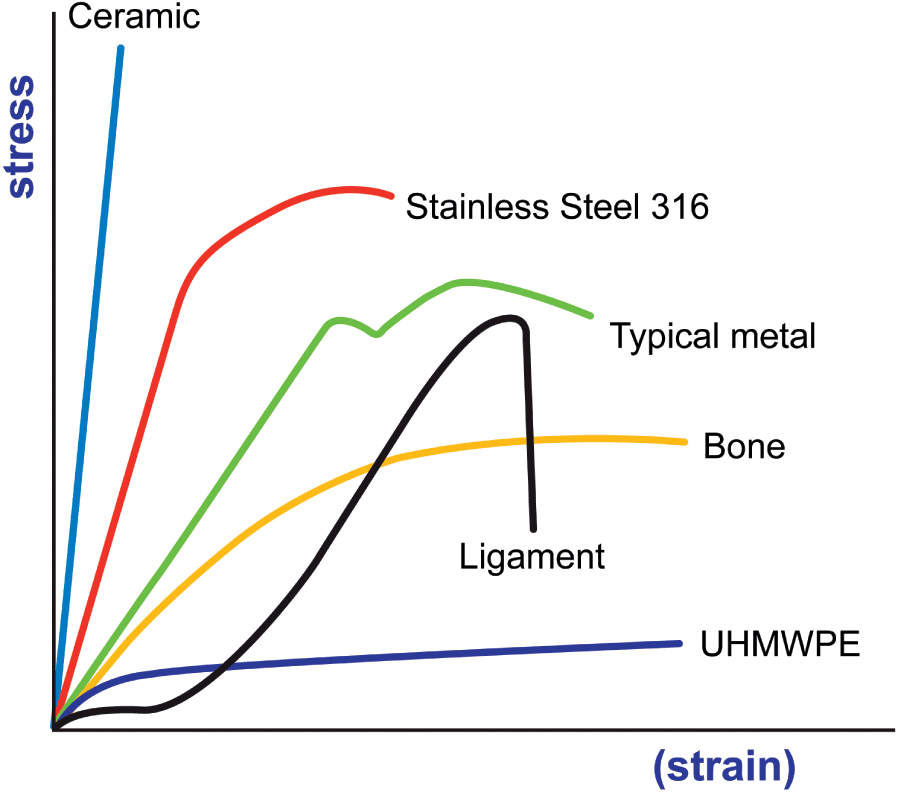
With a very short elastic region but highly capable of supporting huge stresses. Represents straightening of the crimped ligament fibrils. Derived from axially loading an object and plotting the stress verses strain curve. After plotting the stress and its corresponding strain on the graph we get a curve and this curve is called stress strain curve or stress strain diagram.
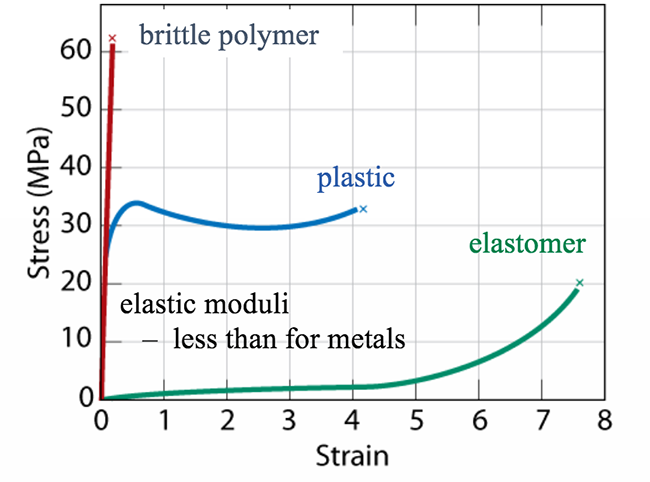
As pores increase strength decreases. Stress strain curve for ceramic vs metal. Occurs when crack propagation starts polymers. This does not however imply softening by alloying.
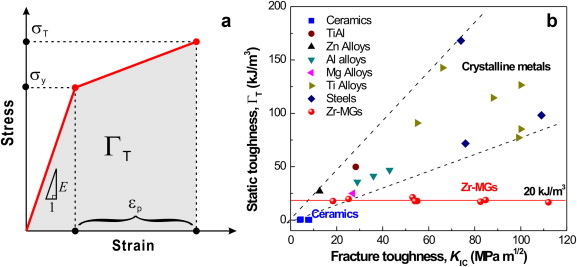
1 ni co as a function of composition. The zone where a material will return to its original shape for a given amount of stress toe region applies to a ligaments stress strain curve. Tensile tests of brittle ceramics are usually not performed. Restricting or hindering dislocation motion makes a material harder and stronger prevents slip which slows down plastic deformation and increases yield strength.
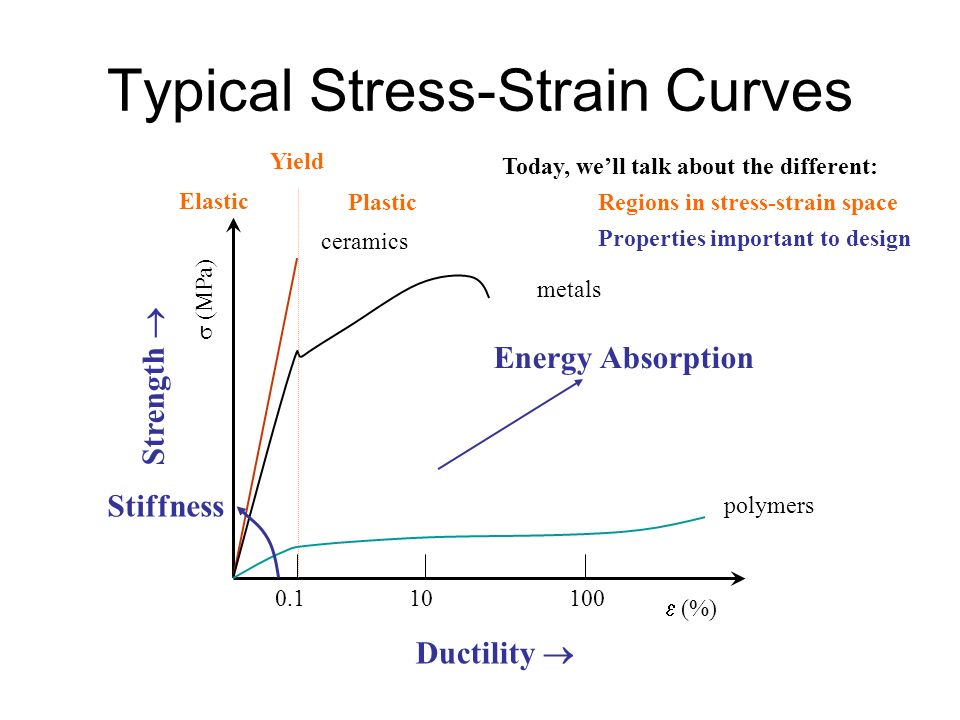
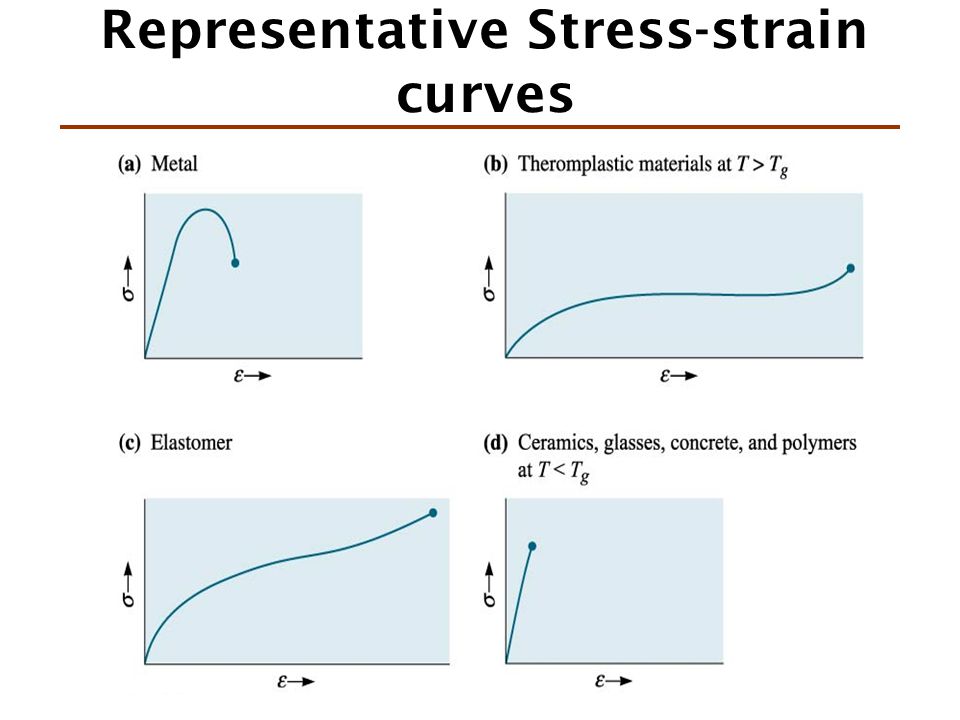
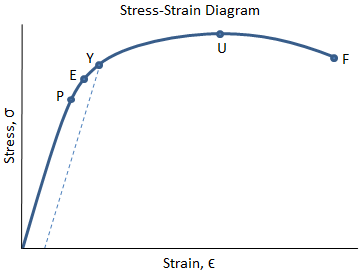
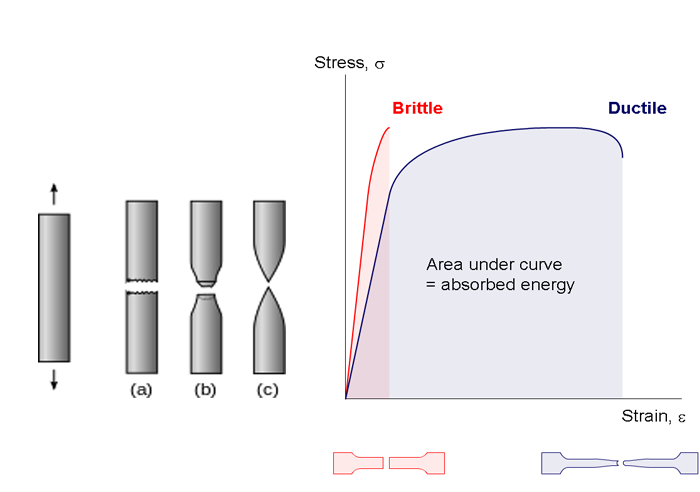
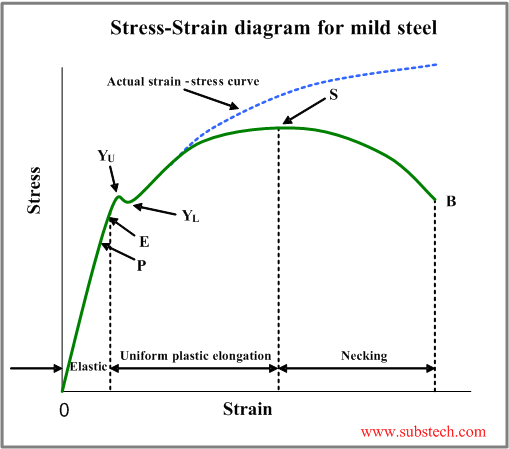
Occurs when noticeable necking starts ceramics. Stress strain curve is the plot of stress and strain of a material or metal on the graph. In engineering and materials science a stress strain curve for a material gives the relationship between stress and strain it is obtained by gradually applying load to a test coupon and measuring the deformation from which the stress and strain can be determined see tensile testing these curves reveal many of the properties of a material such as the young s modulus the yield strength. Yielding starts at c and ends at d.
It is difficult to shape these materials into the proper test structure difficult to grab the brittle material without breaking it and it is difficult to align the test samples to avoid bending stresses. Reason behind strengthening mechanisms. In this the stress is plotted on the y axis and its corresponding strain on the x axis. Stress strain curves for two brittle materials.
2 stress strain curve for ceramics. 1 metals al alloy stress strain curve. The engineering stress strain curve does not give a true indication of the deformation characteristics of a metal because it is based entirely on the original dimensions of the specimen and these dimensions change continuously during the testing used to generate the data. Elastomers are the ones that strains more w a lower stress.
And finally analogous to ceramics are the stiff fibers and rigid plastics.